It’s scarier in a theater! Go check it out
Building a Retro CRT Effect: From Shadertoy to Baselight Matchbox Shader
Hey everyone, lately, I've been asked to dive back into the world of retro aesthetics, and one thing that always stands out is the look of old CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) monitors. That characteristic scanline flicker, the subtle noise, and the slight color fringing – it's all part of a nostalgic visual language. I wanted to bring that look into Baselight (last time I did this it was for Mistika. https://www.johndaro.com/blog/2020/10/28/vhs-shader), so I built a custom Matchbox shader that accurately simulates these CRT artifacts. This post breaks down the process, from finding inspiration to creating a user-friendly tool.
The Inspiration: Shadertoy
My journey started on Shadertoy, a fantastic resource for exploring and learning about GLSL shaders. I found a great CRT effect shader (https://www.shadertoy.com/view/Ms3XWH) that captured the essence of the look I was after. It used clever techniques to generate scanlines, add noise, and even simulate chromatic aberration (that slight color separation you see at the edges of objects on old TVs).
However, Shadertoy shaders are self-contained and designed for a specific environment. To make this useful in Baselight I needed to adapt it for the Matchbox framework.
From Shadertoy to GLSL Standard
The first step was to "translate" the Shadertoy-specific code into standard GLSL. This involved a few key changes:
mainImagetomain: Shadertoy uses a function signaturemainImage(out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord). Standard GLSL, and Matchbox, usevoid main(void). We also replacefragCoordwith the built-ingl_FragCoordand output the color togl_FragColor.Uniform Inputs: Shadertoy provides inputs like
iResolution(screen resolution) andiChannel0(the input texture) automatically. In Matchbox, we need to explicitly declare these asuniformvariables:adsk_result_w,adsk_result_h, andsrc, respectively. We also addediTimeas a uniform to control animation.Texture Sampling: Shadertoy's
texturefunction becomes the standardtexture2Din GLSL.
Here's a snippet illustrating the change:
Shadertoy:
void mainImage( out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord )
{
vec2 uv = fragCoord.xy / iResolution.xy;
// ...
vec4 tex = texture(iChannel0, uv);
fragColor = tex;
}
Standard GLSL (for Matchbox):
uniform float adsk_result_w;
uniform float adsk_result_h;
uniform sampler2D src;
void main (void)
{
vec2 uv = gl_FragCoord.xy / vec2(adsk_result_w, adsk_result_h);
// ...
vec4 tex = texture2D(src, uv);
gl_FragColor = tex;
}
Making it Controllable: Matchbox XML
The real power of Matchbox comes from its ability to expose shader parameters as user-adjustable controls. This is done through an XML file that describes the interface. I wanted to give users control over the key aspects of the CRT effect:
Scanline Width: How thick the scanlines appear.
Noise Quality: The granularity of the vertical noise (lower values create more distinct lines).
Noise Intensity: The amount of horizontal jitter.
Scanline Offset: The intensity of the vertical scanline displacement.
Chromatic Aberration: The strength of the color fringing.
Time: The speed of the animation.
To achieve this, I did the following:
GLSL Changes: In the GLSL code, I replaced the
const floatvariables that controlled these parameters withuniform floatvariables. This is crucial – it tells Matchbox that these values can be changed externally.
// Before (hardcoded): const float range = 0.05; // After (Matchbox controllable): uniform float scanlineRange;
XML Creation: I created an XML file (with the same name as the GLSL file) that defines the controls. Each control is specified using a <Uniform> tag. The most important attribute is Name, which must match the corresponding uniform variable name in the GLSL code.
<Uniform Max="0.1" Min="0.0" Default="0.05" Inc="0.001" ... Name="scanlineRange"> </Uniform>
The XML also includes attributes like DisplayName (the label in the Baselight UI), Min, Max, Default, Tooltip, and layout information (Row, Col, Page). These define how the control appears and behaves in Baselight.
Putting it All Together
The final step was to place both the .glsl and .xml files in the usr/fl/shaders directory. Baselight automatically recognizes the shader and makes it available in the Matchbox node. Pro tip, my shaders directory is a link to a network location. This way all the Baselights can share the same shaders and it makes updating easier.
Now, when I add a Matchbox node and select the CRT effect, I get a set of sliders and controls that let me tweak the look in real-time. I can easily adjust the scanline thickness, add more or less noise, and dial in the perfect amount of retro goodness.
Download the Files
You can download the complete GLSL and XML files for this Matchbox shader here:
Conclusion
This project was a great upgrade to my GLSL knowledge, demonstrating how to take a cool shader effect from a platform like Shadertoy and adapt it into a practical, user-friendly tool for Baselight. The combination of GLSL's power, speed, and Matchbox's flexibility opens up a world of possibilities for creating custom effects that can be used through out the entire post pipeline. It might be old tech but still very useful today. I hope this breakdown inspires you to experiment with your own implementation. Let me know what you think, and feel free to share your own shader creations!
Cheers to "The Sea Beast" Best Animated Feature Film Nomination!
Sending a big cheers and congratulations to Netflix and The Sea Beast crew for their nomination today. The film is a beautiful culmination of an elite group of artists' fantastic work. I am super grateful and proud to have been a part of the team.
Cheers to "The Sea Beast" Best Animated Feature Film Oscar Nomination!
Flippers crossed for a win on the day!
Best Animated Feature Film Nominations
“Guillermo del Toro’s Pinocchio,” Guillermo del Toro, Mark Gustafson, Gary Ungar and Alex Bulkley
“Marcel the Shell With Shoes On,” Dean Fleischer Camp, Elisabeth Holm, Andrew Goldman, Caroline Kaplan and Paul Mezey
“Puss in Boots: The Last Wish,” Joel Crawford and Mark Swift
“The Sea Beast,” Chris Williams and Jed Schlanger
“Turning Red,” Domee Shi and Lindsey Collins
DC League of Super Pets
Super excited for everyone to check out the latest from Warner Animation. DC League of Super Pets is a super fun romp expertly animated by the talented team at Animal Logic.
Toshi the Wonder Dog!
Anybody that has ever had a pet is going to love this movie.
Post services provided by Warner PPCS include an ACES HDR picture finish and sound. Truly a post-production one-stop-shop.
The project was supervised by Randy Bol. The great thing about working with Randy is we have a level of trust that has been built over many other projects collaborating together. There is definitely a shorthand when both of us are in the suite. One of the best post sups you’ll work with plus just a good dude too.
Color was supervised by co-director Sam Levine. This guy was cracking me up every session. Not only was he hilarious, but damn, what an eagle eye. I was sort of bummed when our time together ended.
A big thanks to Paul Lavoie and Leo Ferrini too for keeping the ship afloat. I would be drowning in a pile of pixels without these guys.
Now go see DC League of Super Pets only in theaters… Preferably a Dolby Cinema one.
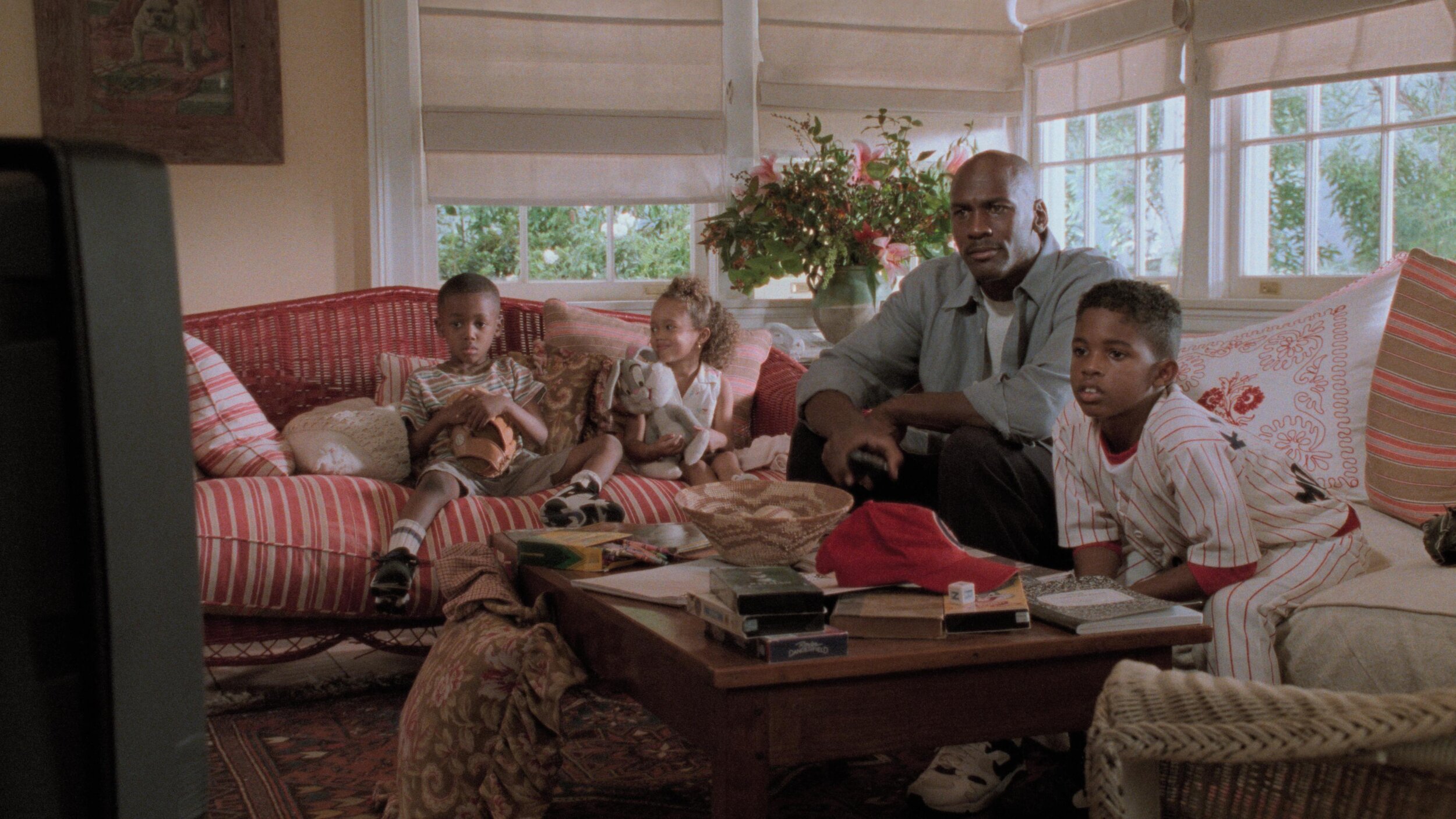
The Sea Beast Teaser | Netflix
Here is a first look at the latest project from Chris Williams and Netflix that I graded. An awesome project with an animation A-team. Let me know what y’all think.
Looking Back on 2021
I wanted to take a quick moment to look back on all the great work that the team and I accomplished this year. There were a ton of fantastic projects with amazing filmmakers. Paul Lavoie and I also got the opportunity to take a second crack at some of our earlier work by giving it a 4k HDR makeover. Have we really been at it that long?
I owe a huge debt of gratitude to Leo Ferrini and Paul Lavoie for their dedication to our clients and never compromising on quality. They keep me honest. I’m very grateful to have partners like this A-team. Our operation is strong here on the Warner lot. Looking forward to what will come in 2022!
2021 New Theatrical and Remasters
Happy New Year and happy grading everyone!
-JD
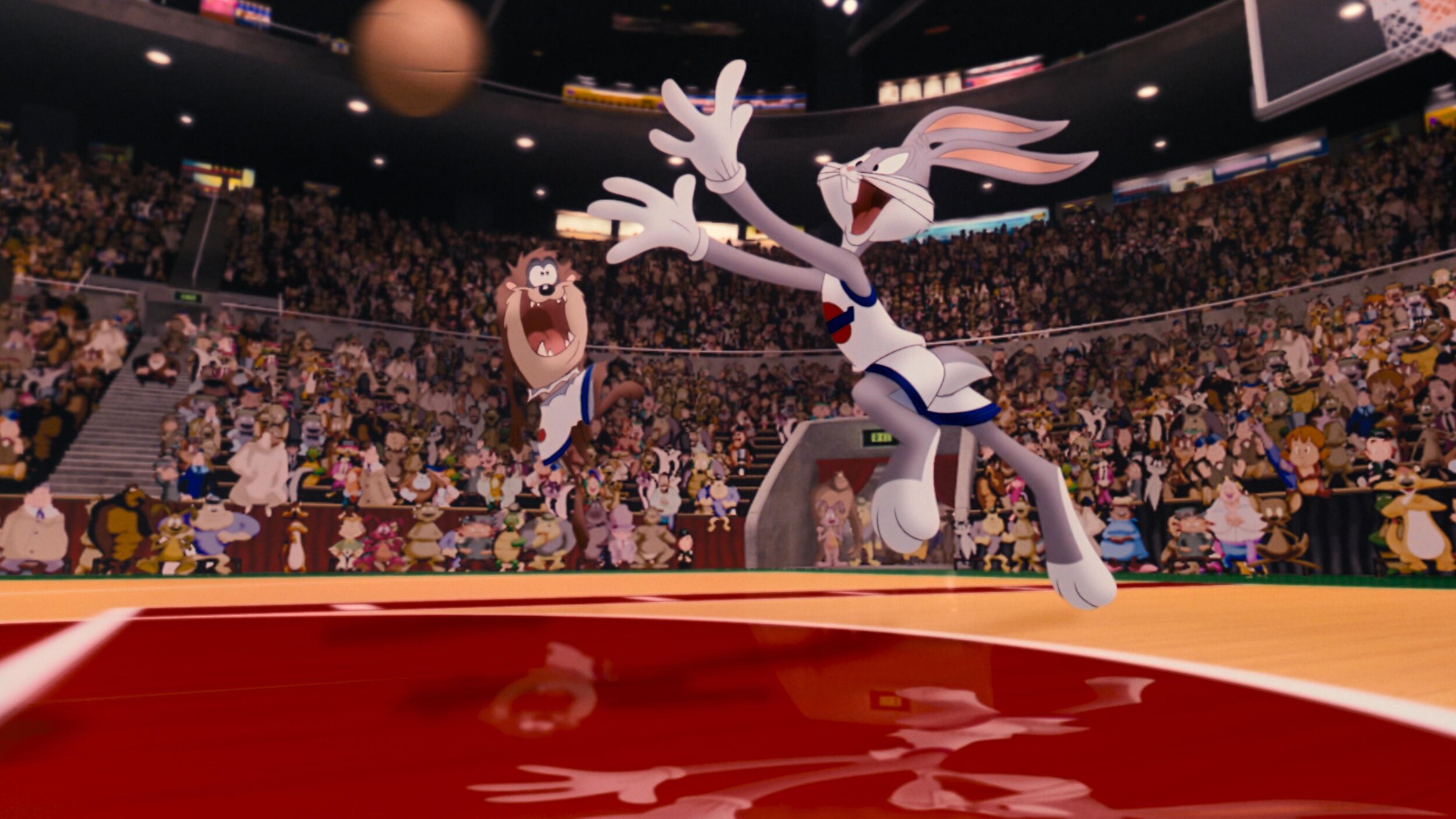
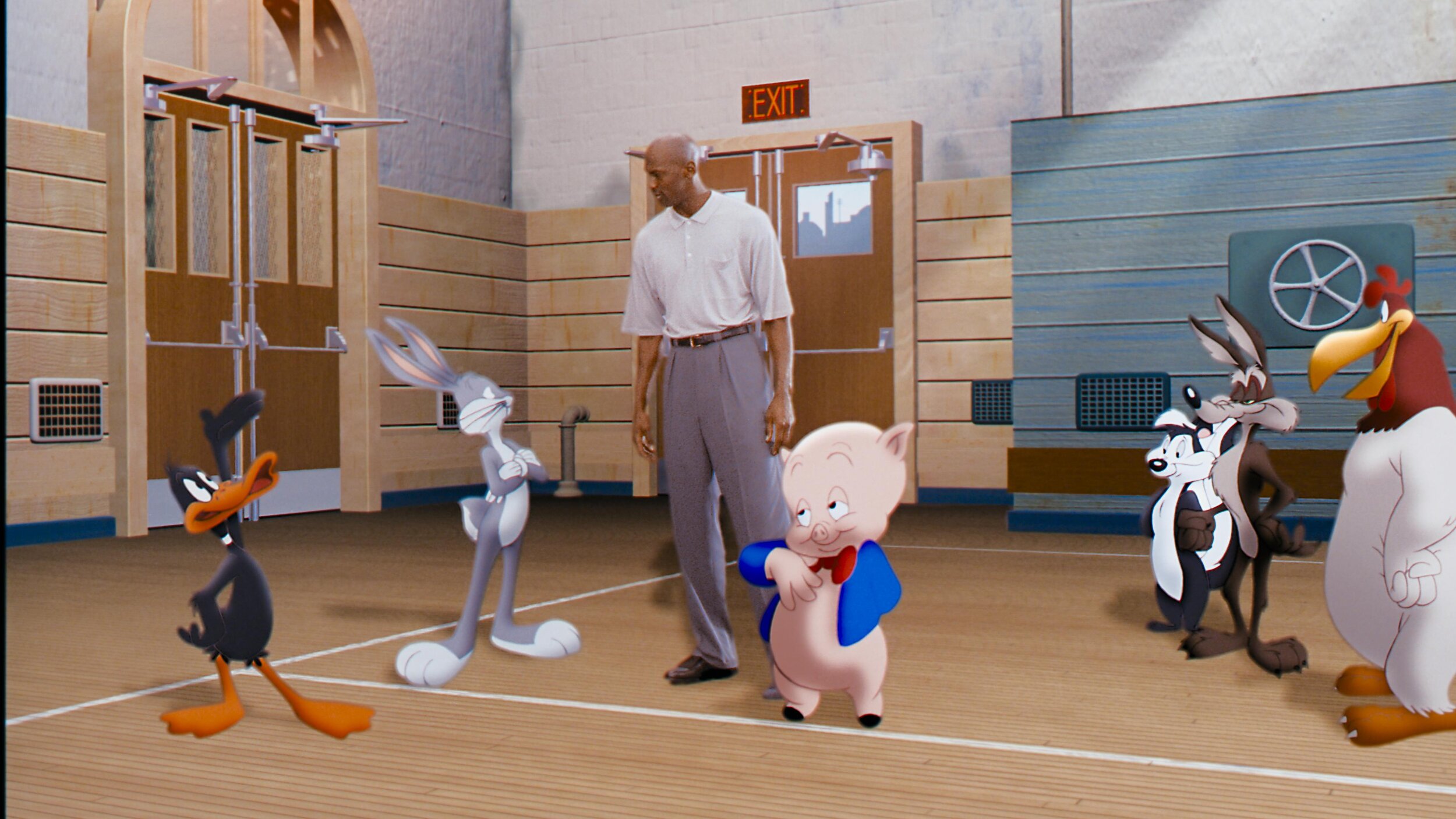
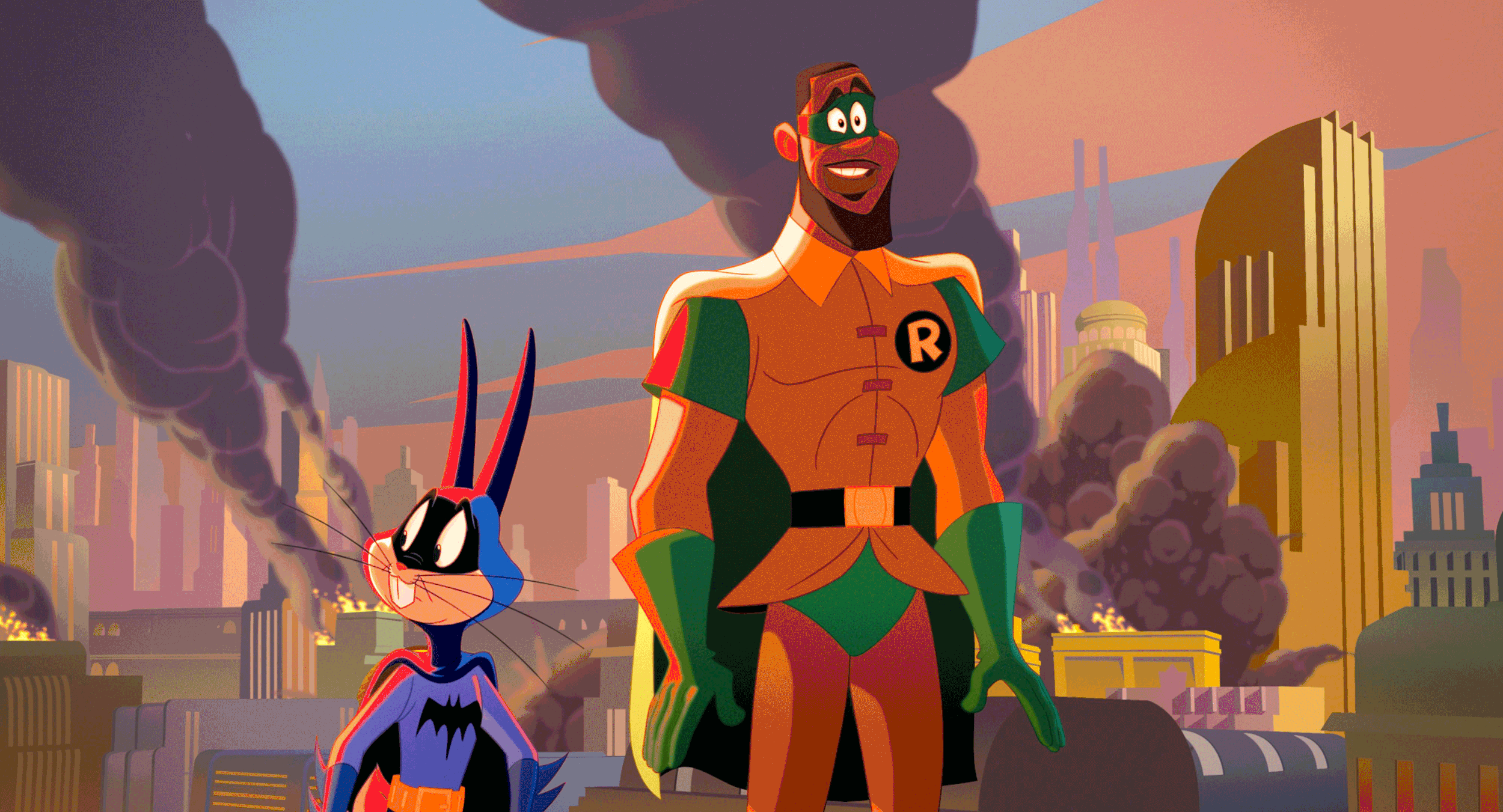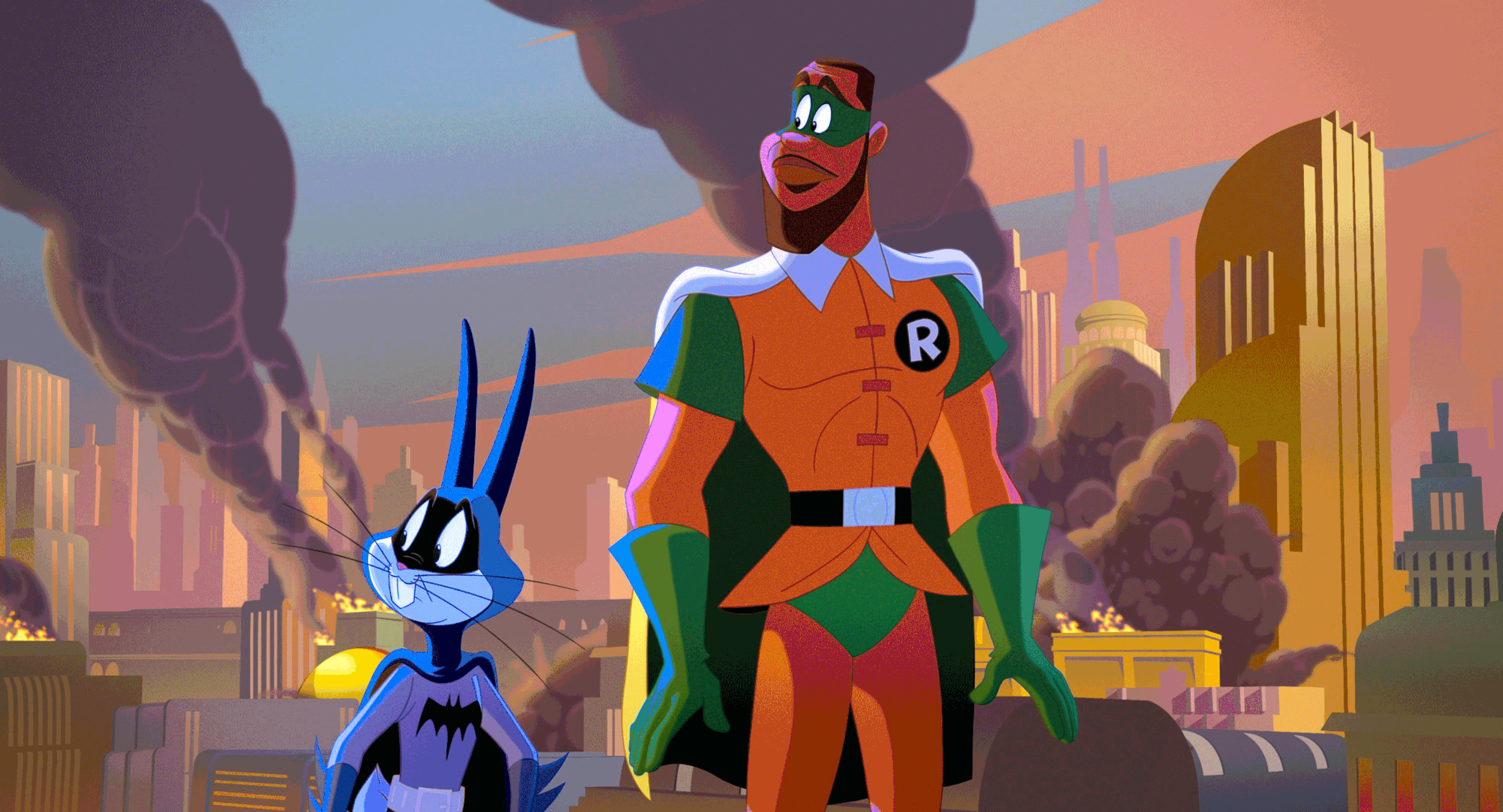
Space Jam: A New Legacy - Multiple Worlds, Multiple Deliveries.
Hey Everybody! Space Jam: A New Legacy directed by Malcolm D. Lee is out today. I wanted to take a second to highlight the super slick color workflow which allowed us to work on multiple versions concurrently.
Capture
Space Jam: A New Legacy was masterfully lensed by Salvatore Totino. The two primary capture mediums were 35mm Kodak film and the entire lineup of Arri cameras, mainly the LF. The glass used was Zeiss Supremes and Master Primes. There were also a handful of scans from archival films which were used as plates for animation.
VFX
ILM was running point for the VFXs on this show. Grady Cofer and his team were a dream to work with. There is a reason ILM continues to be the best in class. The knowledge and expertise ILM employs is second to none. Early on Grady connected me with their head of color science, Matthias Scharfenberg. I thought I knew what I was doing when it comes to color science until I saw what Matthias had going on with CTL and Nuke. I learned a lot from our chats. He was super gracious in sending over his Nuke scripts which allowed me to build a Baselight transform that matched ILM’s pipeline. This insured a one-to-one representation of their stellar work.
Two Worlds, One Grade
The show can basically be broken down into two looks. In “Space Jam: A New Legacy” there is the real-world and the Warner Bros Serververse.
We chose an analog celluloid vibe for the real world. The Serververse has a super clean, very 1s and 0s look to it. Most of the real world is shot on film or is Arri Alexa utilizing film emulation curves paired with a grain treatment. Some sequences have a mix of the two. Let me know if you can tell which ones😉.
The look of the digital world changes depending on where the characters are in the Serververse. The base look of the Serververse is the vanilla ACES ODT with restricted primaries in the mid-tones complimented by exaggerating the saturation for highly saturated colors.
All the other looks are riffs off this base LMT with the exception of the library classics. These were graded to look like their existing masters and the new footage was matched in.
Multiple Deliverables, One Timeline
The challenge of this show, beyond the sheer number of VFX and moving parts, was the delivery schedule. The Post Supervisor Lisa Dennis asked to have the theatrical version and the HDR video versions delivered days apart. To hit the dates requested, I graded simultaneously in HDR and SDR. I did most of the heavy lifting in HDR PQ 1000nits. Then I trimmed at 14FL to ensure the reel was ready for filmmaker review. Poping back and forth between outputs was made possible by two great tools. Firstly, I used ACES 1.1 color management to normalize all the different sources into one grading space.
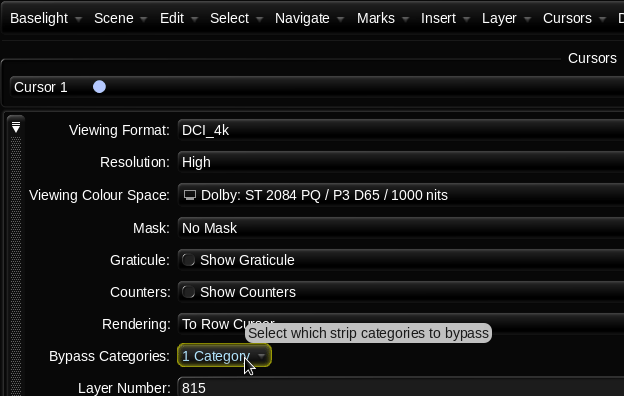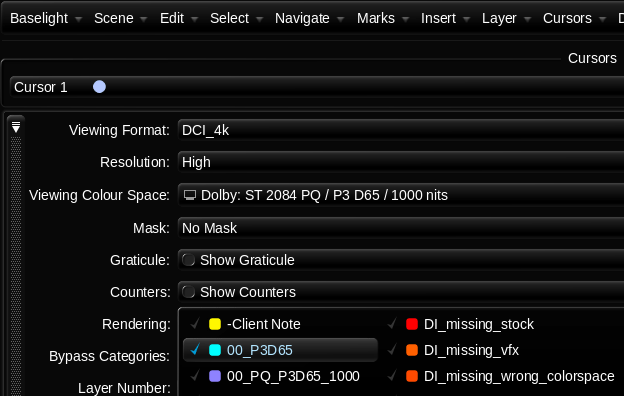
Secondly, I used Baselight’s “Bypass Categories” functionality to if/then the timeline. Basically, I had one timeline that would represent itself differently depending on the output selected. Different layers were toggled for different sources and outputs. The LMTs used often had SDR and HDR versions to further exacerbate the combinations. This was a critical hurdle to overcome and the Baselight gave me the tools to accomplish the organization of a very complicated timeline with ease.
Approvals
The Color sessions were supervised by Malcolm, Sal, and Bob Ducsay. We used Nevion and ClearView for remote sessions, but most of the work was done in-person on the lot here in Burbank. The Animated sequences were supervised by Spike Brandt and Devin Crane. These guys are animation heavyweights, so very cool to be in such good company for an animation nerd like me.
Most of the tweaking on the animation was for continuity fixing. A few of the shots we composited for final in the Baselight. This gave Devin and Spike a little extra creative freedom than a baked shot would have.
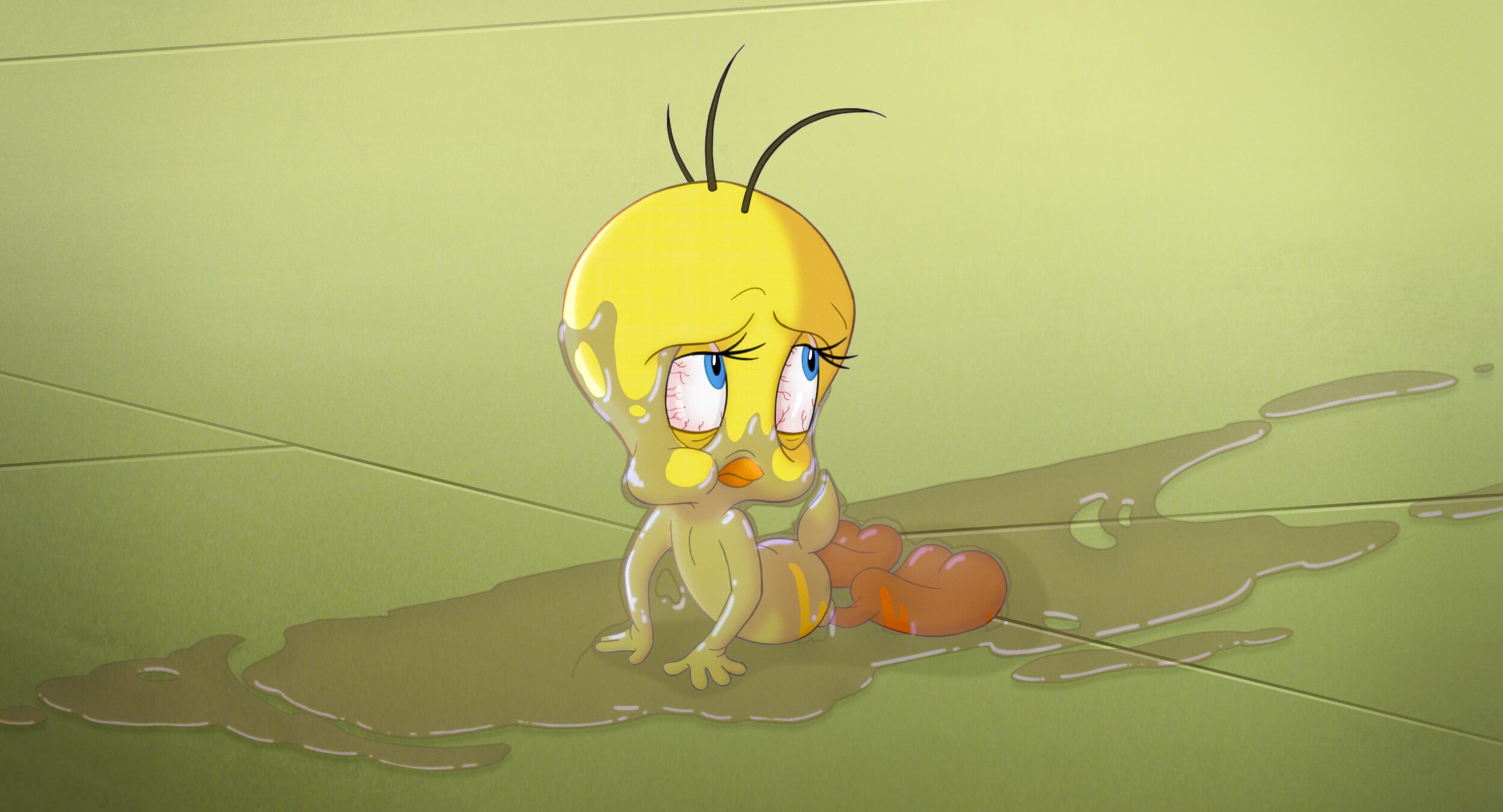
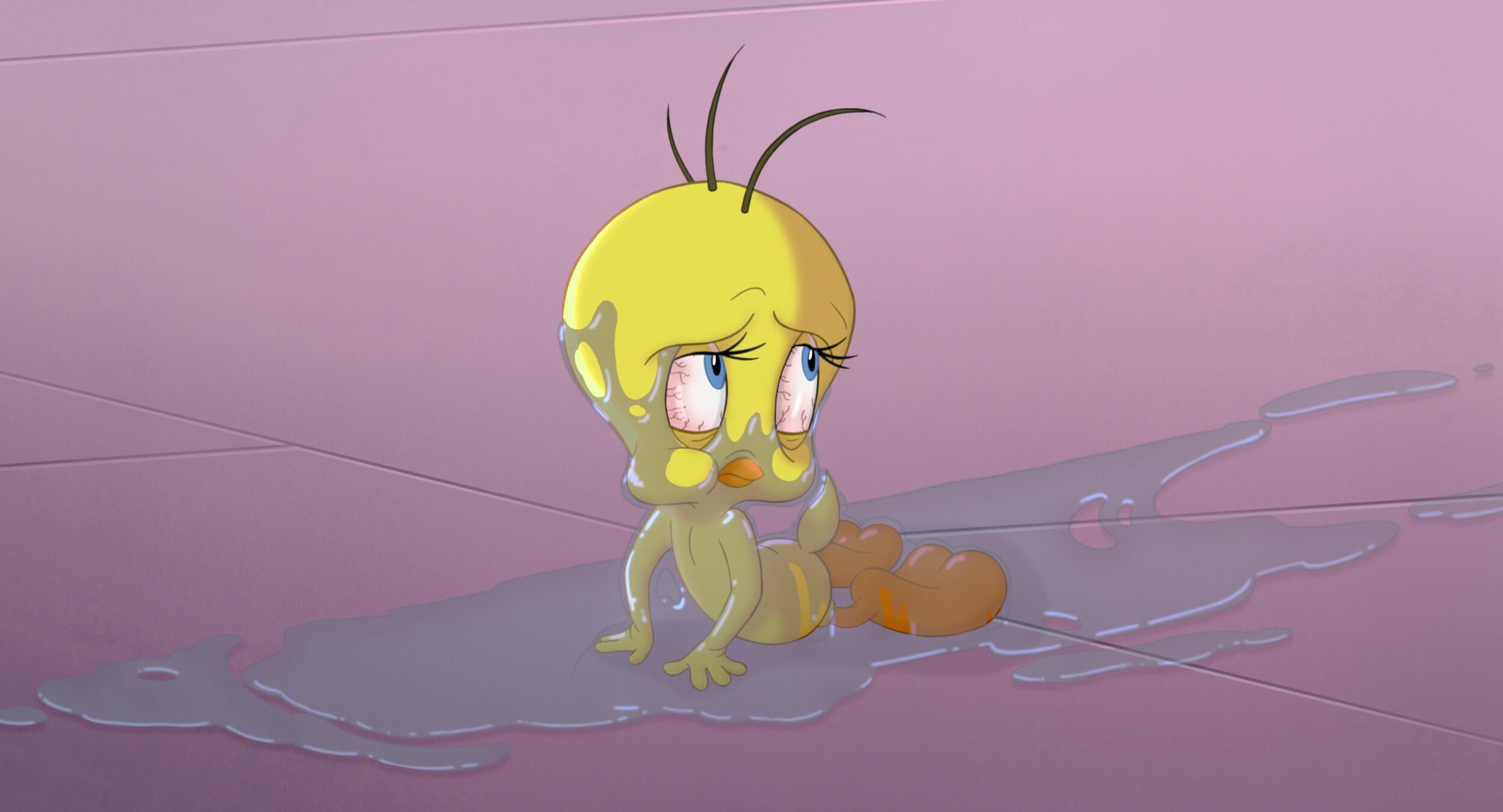
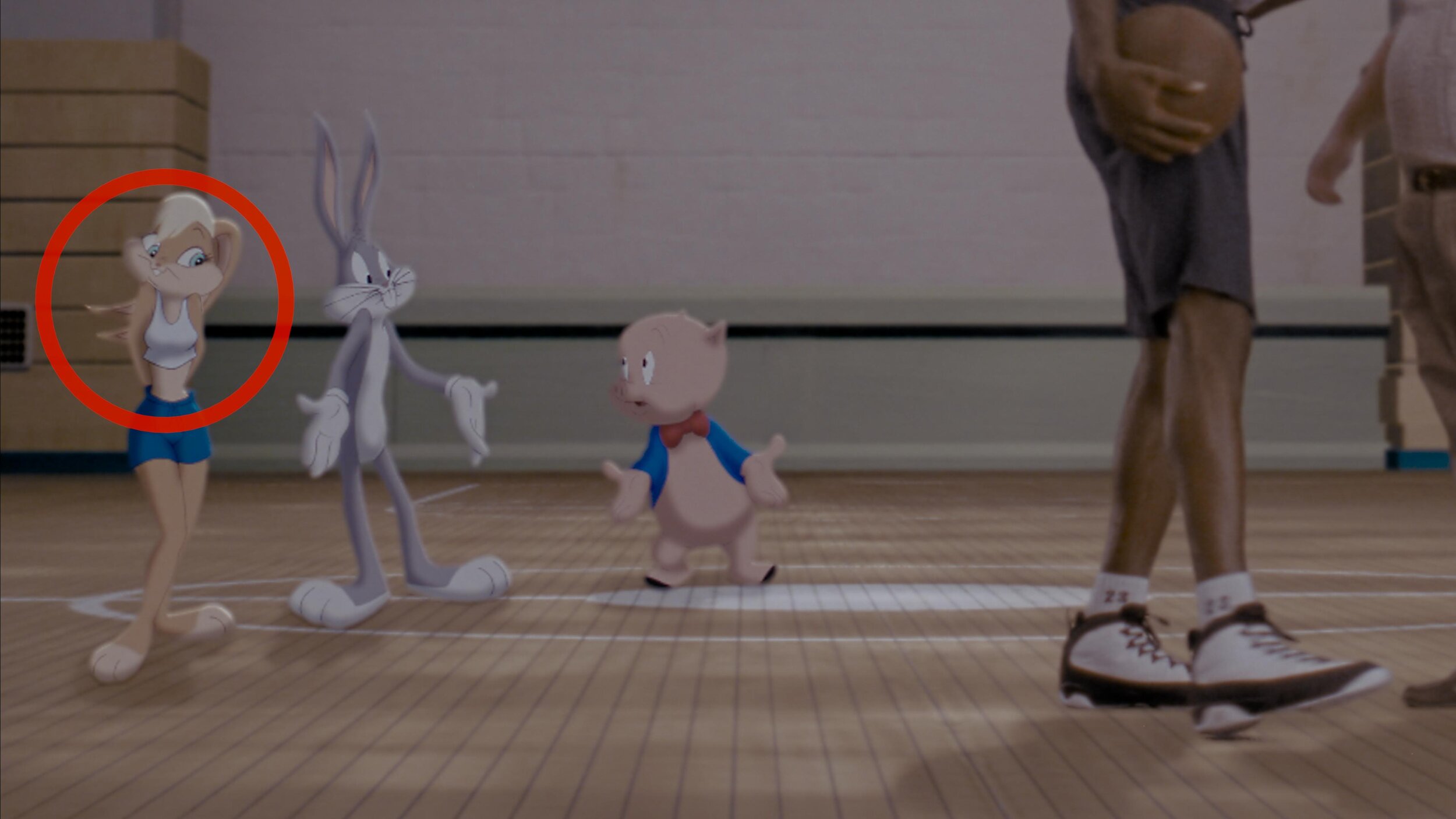
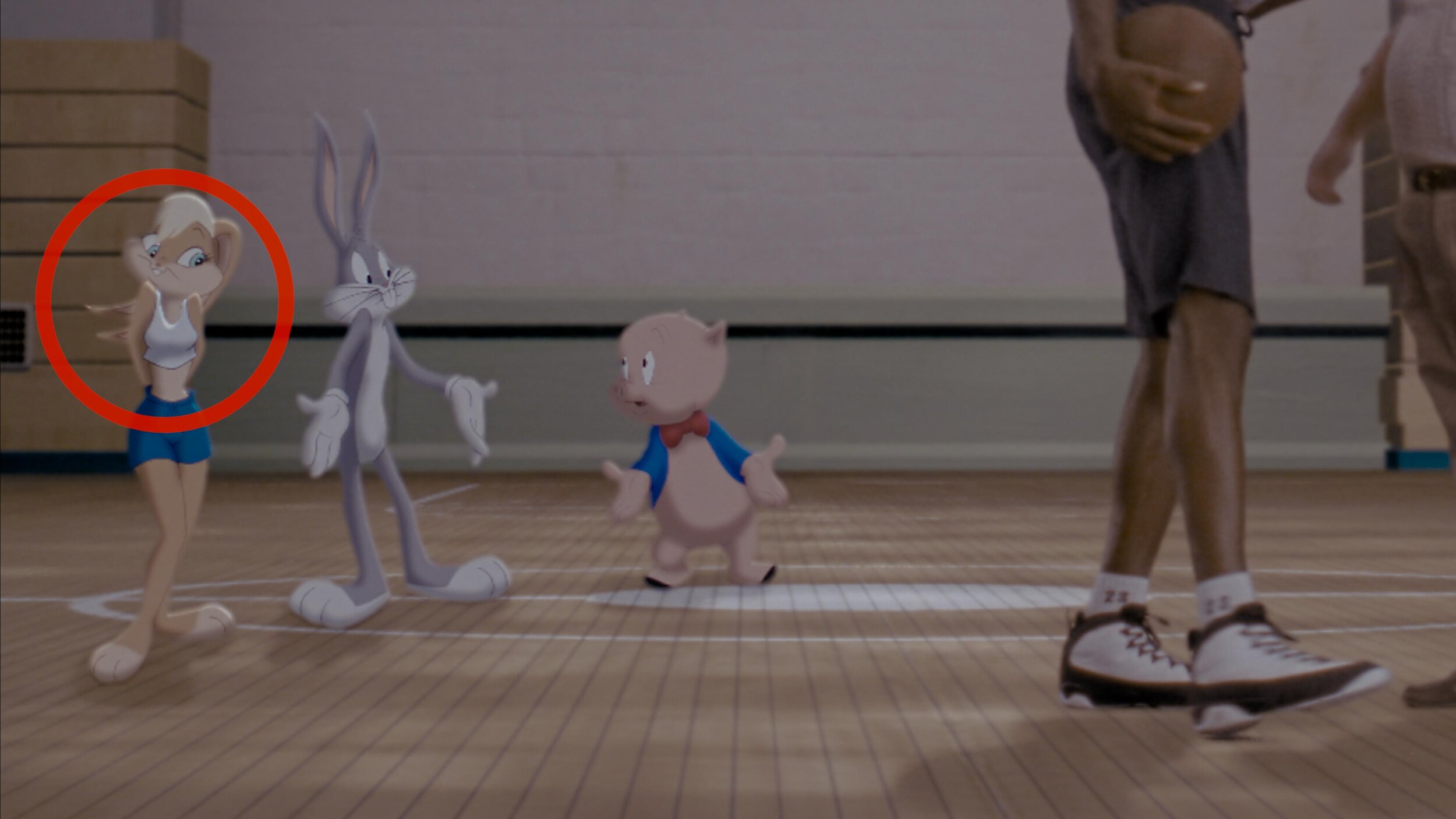
Reference for Tweety’s floor
After all the color decisions were made, Malcolm had his final pass and the masters were created. All deliverables from that point were sub-masters from the hero PQ deliverable. These included deliverables such as the Dolby Vision Theatrical version and 709 SDR version derived from the Dolby XML metadata.
Go See It!
Thanks for reading how the look of this candy-colored revival came together. Working on Space Jam was a wild ride. I had to tap into my background in photochemical film processing and knowledge of the latest digital grading techniques to create unique looks for all the different cinematic worlds visited. The film is a nostalgic love letter to the rich history and legacy of the Warner Bros. Studio. I couldn't be more proud of the Warner Color team, especially Leo Ferrini and Paul Lavoie. A big thanks to you guys! Putting this film together was a monumental task and I am ecstatic with end result. Check it out in theaters and on HBO Max today!
Best Practices: Restoring Classics
2020 - The year of Restorations
Now that we seem to be on the other end of the pandemic, I wanted to take a moment to look back on some of the projects that kept me busy. Restorations were the name of game during covid times. With productions shut down and uncertainty in the theatrical marketplace, I had time in my schedule to breathe new life into some of my favorite classics.
Over the last year, I have restored;
Let’s take a look at a couple of these titles and talk about what it means to remaster a film with our contemporary toolset.
The Process
The process for remastering classic titles is very similar to finishing new theatrical work with a couple of additional steps. The first step is to identify and evaluate the best elements to use. That decision is easy for digitally acquired shows from the early 2000’s. In those instances, the original camera files are all that exist and are obviously the best source. Film shows are where it gets particularly ambiguous. There is a debate whether starting from the IP or original negative yields better results. Do we use the original opticals or recreate them from the elements? Black and white seps vs faded camera neg? These questions all need to be answered before you begin the work. Usually I prefer to start with the OCN when available.
Director Scanner
Arri Scan
Scanning
Scanning is arguably the most critical part of the process. Quality and success will live or die by the execution of great scans. Image breathing, movement, and general sharpness are issues to look for when evaluating. Scans should not be pretty but rather represent a digital copy of the negative. In a perfect closed-loop system, a scanned piece of film, once shot back out on a calibrated recorder needs to closely match the original negative.
Digital Restoration
The next step in making an old project shiny and new is to repair any damage to the film from aging or that was inherent in production. this includes painting out splice lines, gate hairs, dirt, and scratches. Film processing issues like breathing or turbulence can also be taken care of in this step. I prefer to postpone flicker removal until the grading step since the contrast will have an effect on the amount of flicker to remove. Some common tools used for restoration include MTI and PF Clean. This work is often outsourced because of the high number of man-hours and labor costs associated with cleaning every frame of film. Some companies that do exceptional restoration work are PrimeFocus and Prasad among others.
Grading
Grading restoration titles is a total sub-discipline from grading as a whole. New theatrical grading starts with references and look development to achieve a certain tone for the film. There is a ton of work that goes into this process. Restoration grading differs since the goal is staying true to that original intent. Not reimagining it. Much like new theatrical grading, a good reference will set you up for success. My preferred reference is a filmmaker-approved answer print. These were the master prints that best represented the filmmakers’ creative intent.
A good practice is to screen the print and immediately set looks for the scans getting as close as possible at 14fl projected. An upgrade to this workflow is to use a projector in the grading suite like a Kinoton. These projectors have remote control and cooling. This allows you to rock and roll the film. You can even freeze-frame and thanks to the built in cooling your film doesn’t burn. Setting up a side-by-side with the film vs digital is the best way to ensure you have a match to the original intent. These corrections need to happen using a good color management system. Aces for example has ODTs for theatrical 48nits which is the equivalent of 14fl. Once you have a match to the original, the enhancement can start.
There would be no point in remastering if it was going to look exactly like the existing master. One great reason to remaster is to take advantage of new advancements in HDR and wide color gamut formats. Film was the original HDR format containing 12 stops of range. The print was the limiting factor, only being able to display 8 of those stops. By switching the ODT to PQ P3D65, we can take advantage of the larger container and let the film display all that it has to offer.
My approach is to let the film land where it was originally shot but tone-mapped for PQ display. This will give you a master that had the original intent of the print but in HDR. I often use an LMT that limits the gamut to that of the emulsion used for original photography. This also ensures that I’m staying true to the film's original pallet. Typically there is some highlight balancing to do since what was white and “clipped” is now visible. Next is to identify and correct any areas where the contrast ratios have been disrupted by the increased dynamic range. For example, if there was a strongly silhouetted shot, the value of the HDR highlight can cause your eye to iris down changing the perception of the deep shadows. In this case, I would roll off the highlights or lift the shadows so the ratio stays consistent with the original. The extra contrast HDR affords is often welcomed but it can cause some unwanted issues too. Grain appearance is another one of those examples.
Grain Management
Film grain is one of those magic ingredients. Just like salt, you miss it when it is not there and too much ruins the dish. Grain needs to be felt but never noticed. It is common for the noise floor to increase once you have stretched the film scan to HDR ranges. Also, the grain in the highlights not previously visible starts to be seen. To mitigate this, a grain management pass needs to be implemented. This can come before the grade, but I like to do this after since any contrast I add will have an effect on the perceived amount of noise. Grain can impart a color cast to your image, especially if there is a very noisy blue channel. Once removed this needs to be compensated for and is a downside of working post grade. It is during this pass that I will also take care of flicker and breathing which the grade also affects. My go-to tool for this is Neat Video. You would think that after a decade of dominance some software company would have knocked Neat off their throne as king of the denoise, but it hasn’t happened yet. I prebake the scans with a Neat pass (since Baselight X doesn’t play nicely with Neat yet.) Next, I stack the Neat’ed scan and the original as layers. This allows me to blend in the amount of grain to taste. The goal of this pass is to keep the grain consistent from shot to shot, regardless of the grade. The other, and most important goal is to make the grain look as it did on the print.
Dolby Trim
After the HDR10 grade is complete, it’s time for the Dolby trim. I use the original 14 FL print match version as a reference for where I want the Dolby trim to clip and crush. Once all the trims have been set, I export out a Dolby XML expecting rec2020 primaries as input. Yes, we graded in P3, but that gamut will be placed into a 2020 container once we export.
Mastering
Once all the work has been completed it’s time to master. Remasters receive the same treatment as new theatrical tiles when it comes to deliverables. The common ones are as follows:
Graded PQ P3D65 1000nit 16bit Tiff Files or ACES AP0 EXRs
Un-Graded PQ P3D65 16bit Tiff files or ACES AP0 EXRs
Graded 2.6 XYZ DCDM 14fl
Graded PQ XYZ 108nit 16bit Tiff Files or ACES AP0 EXRs for Dolby Vision Theatrical
Bt1886 QT or DPX files created from a Dolby XMLIMF PQ rec2020 limited to P3D65 1000nit
Case Studies
Perfect worlds do exist but we don’t live in one. Every job is a snowflake with its own unique hurdles. Remastering tests a colorists abilities across many disciplines of the job. Stong skills in composting, paint, film manipulation, and general grading is what is required to achieve and maintain the original artistic intent. Here are two films completed recently and a bit on the challenges faced in each.
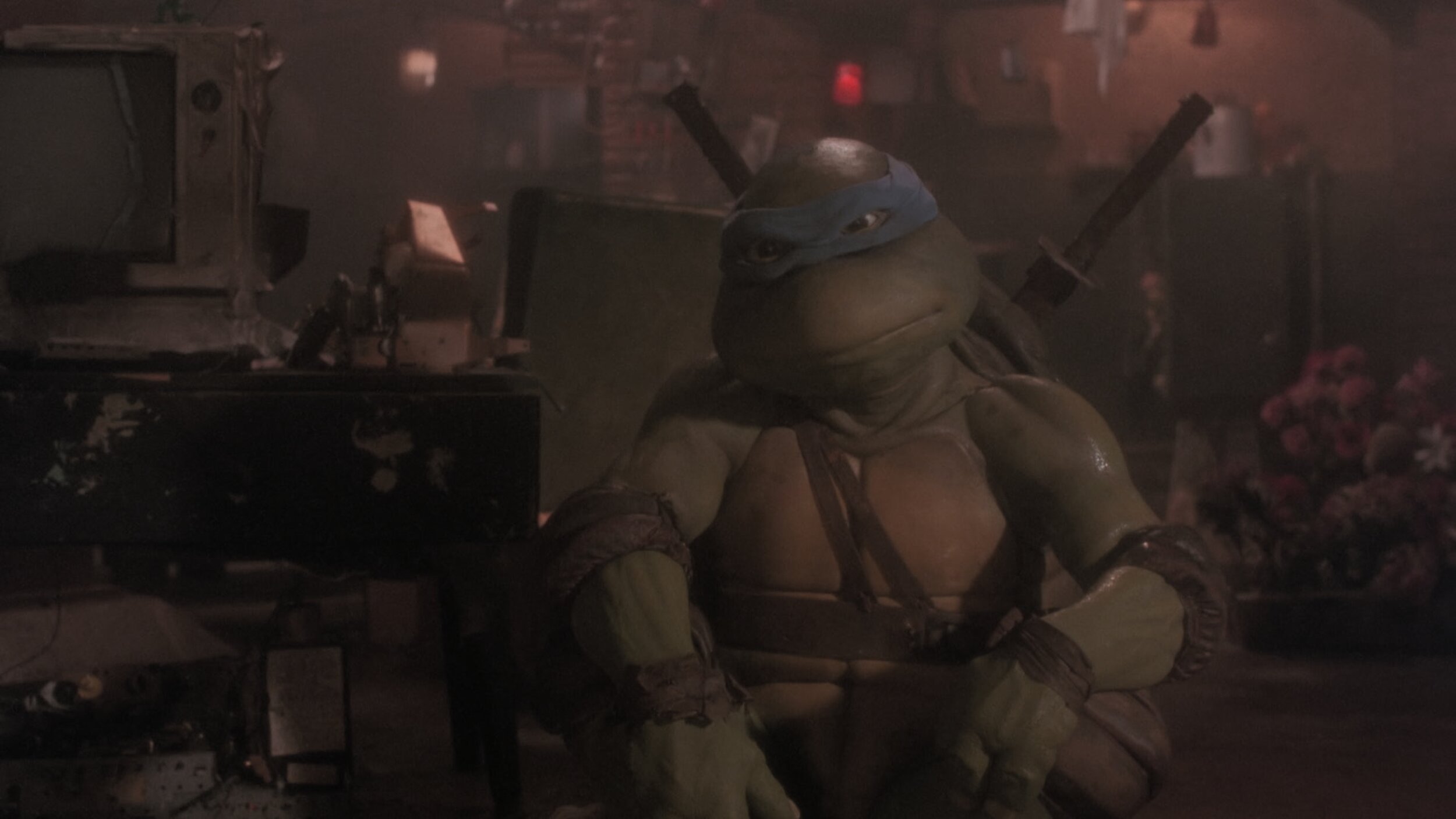
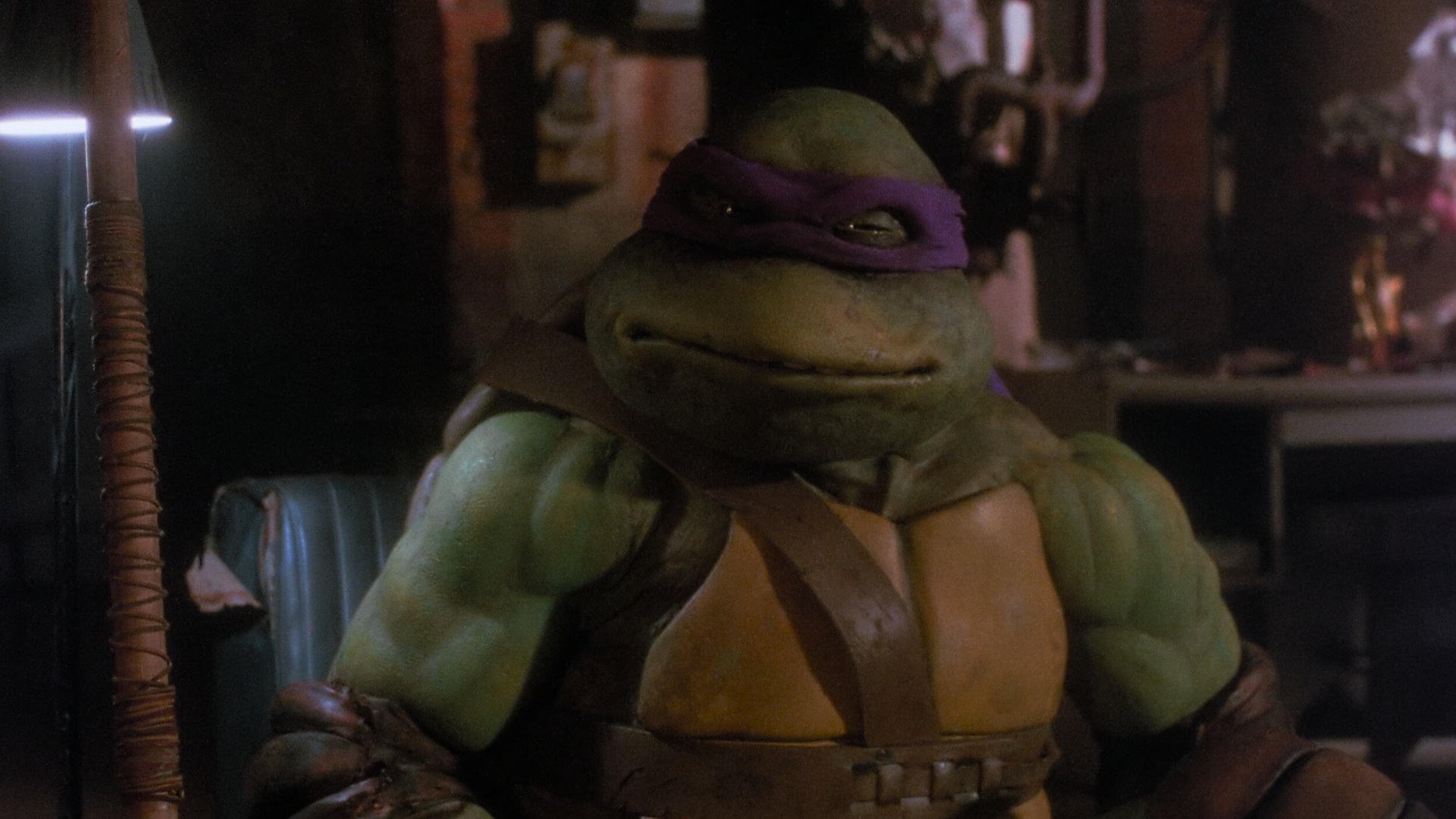
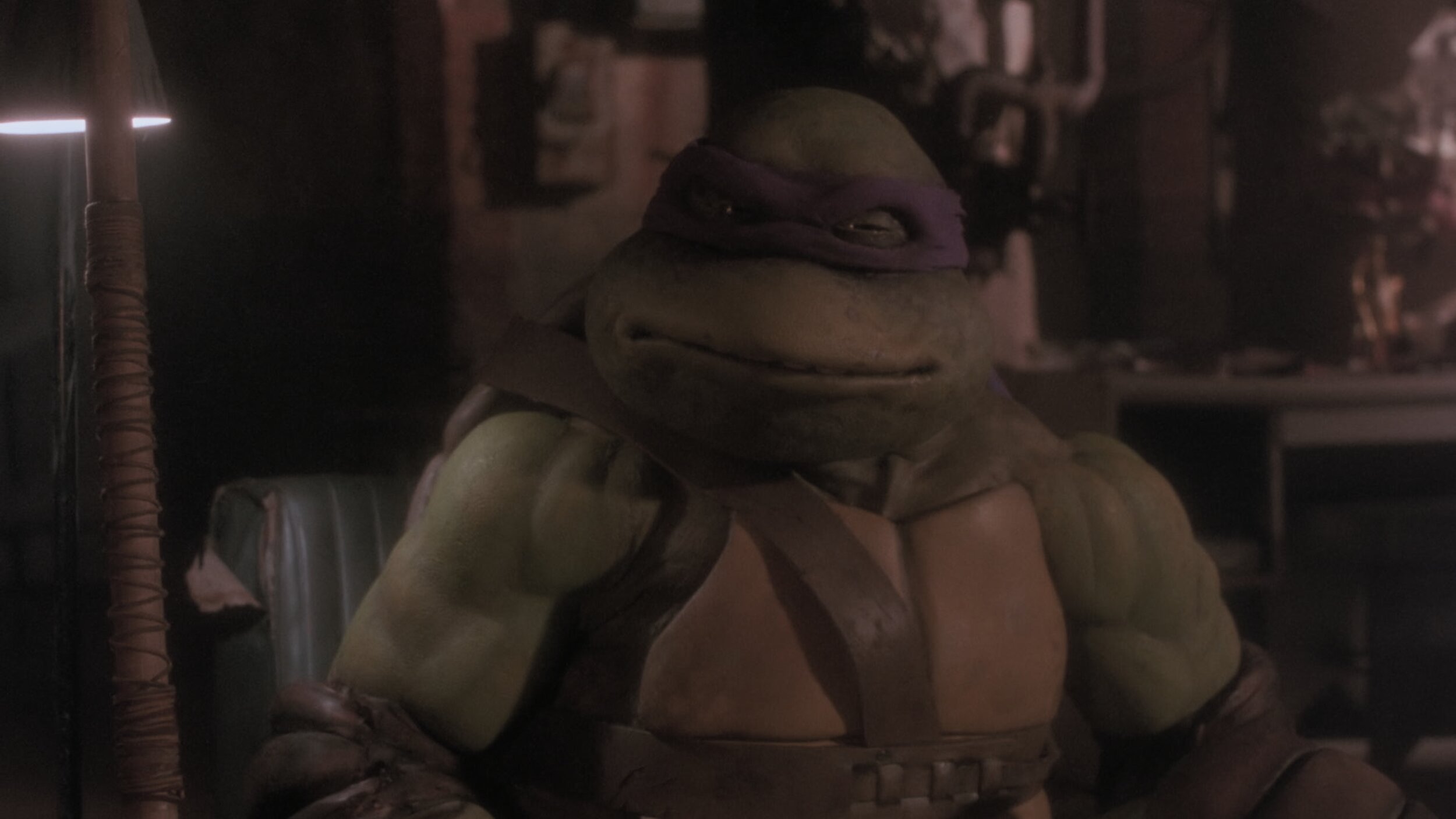
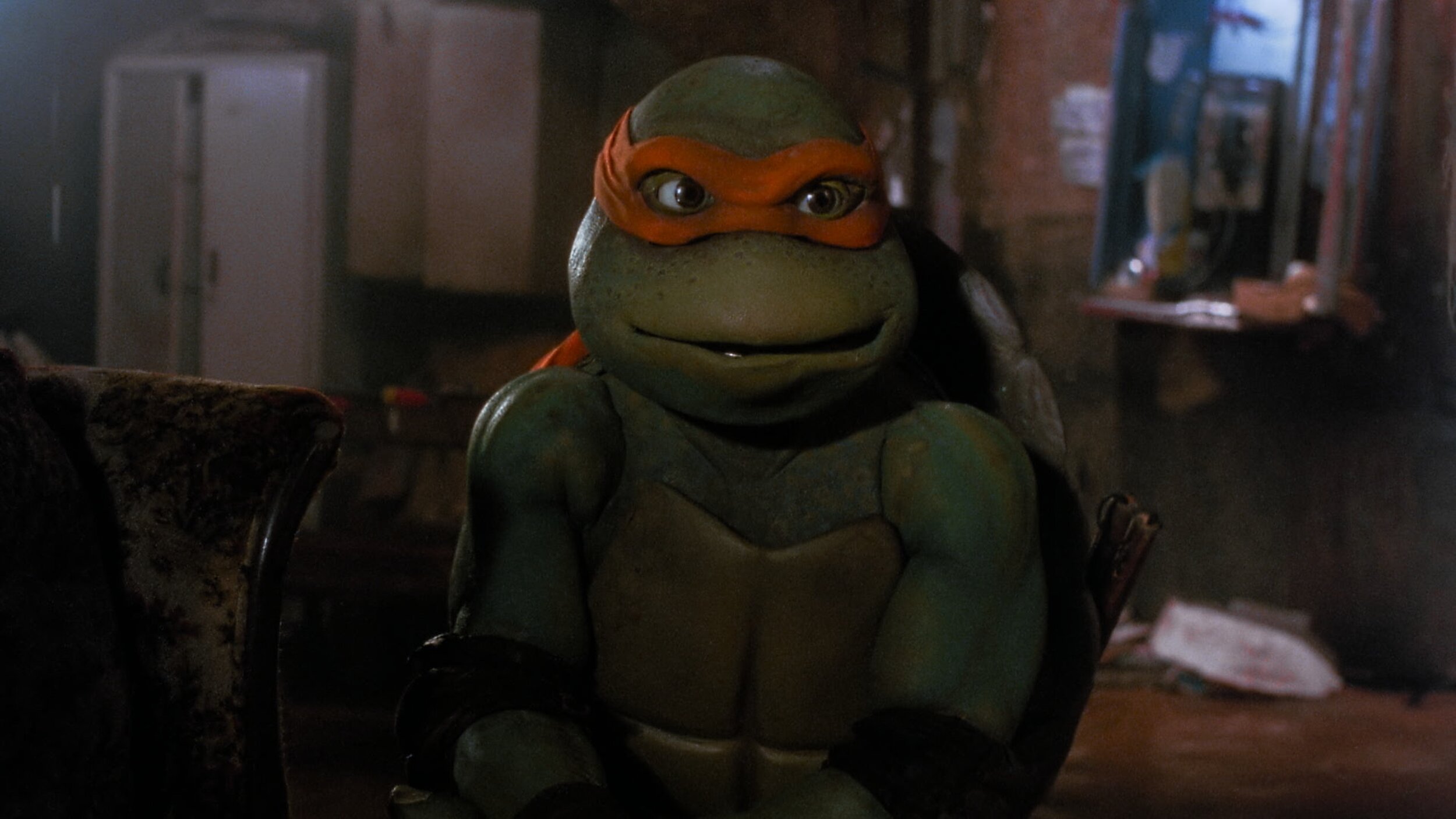
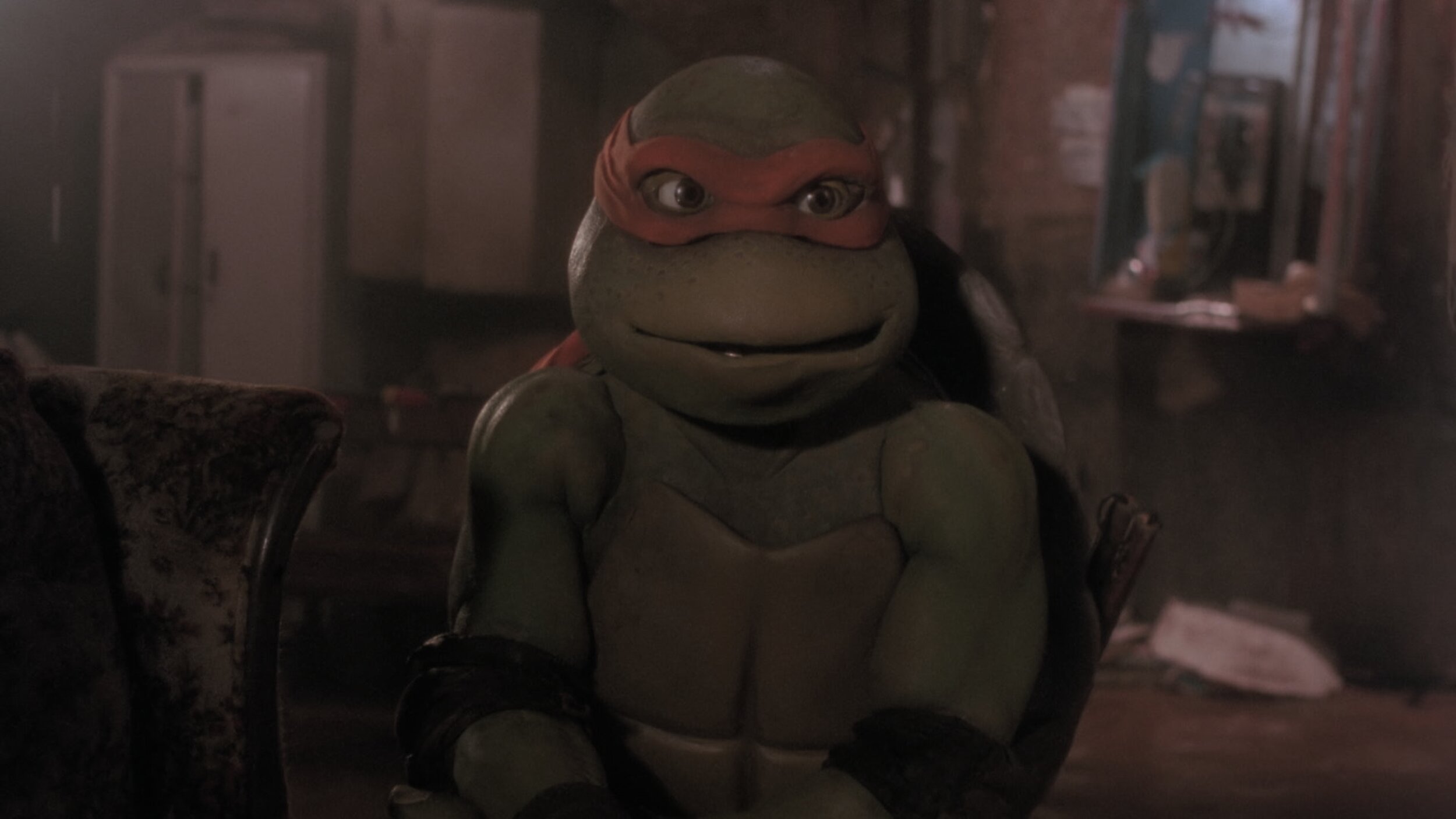
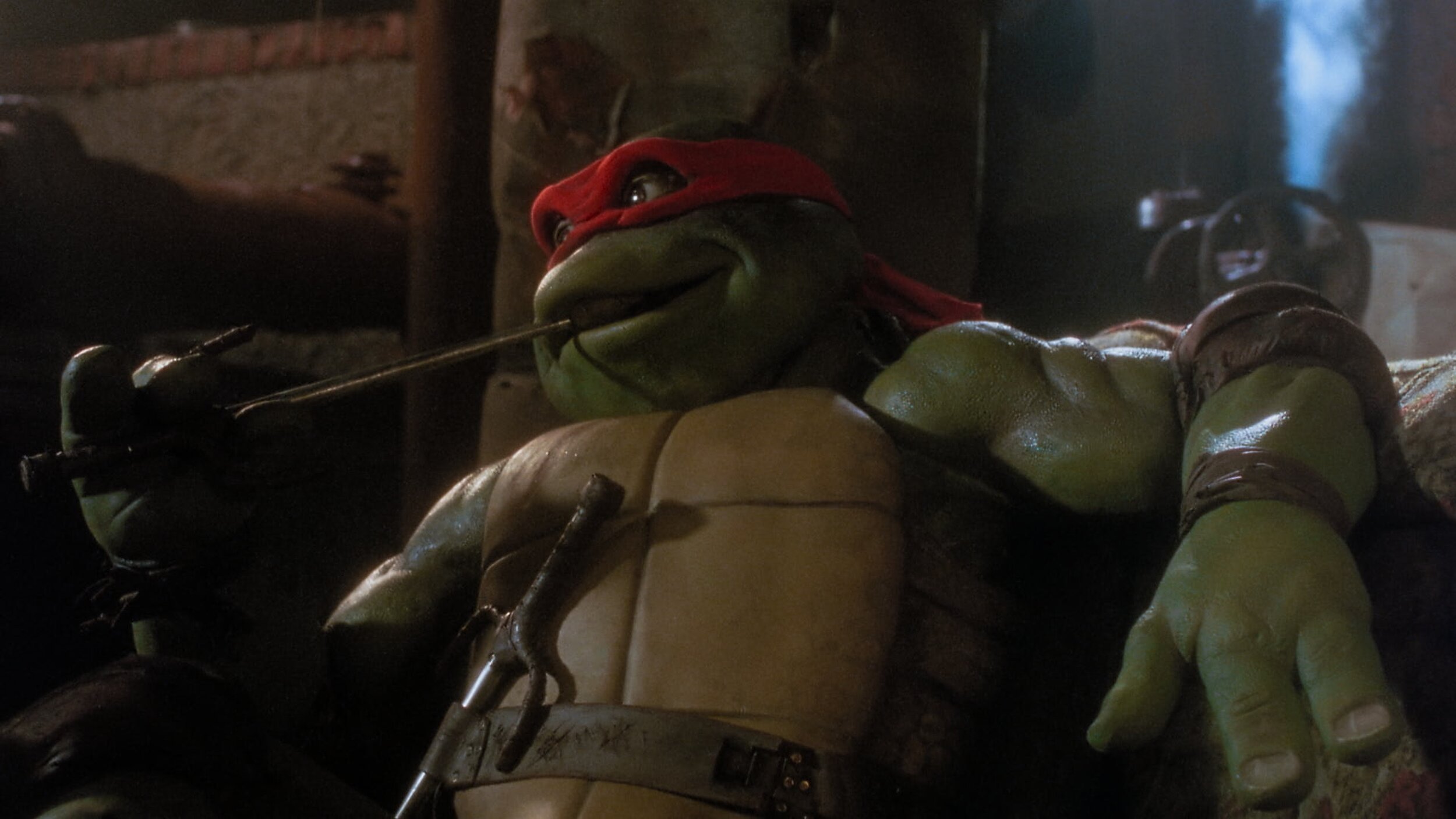
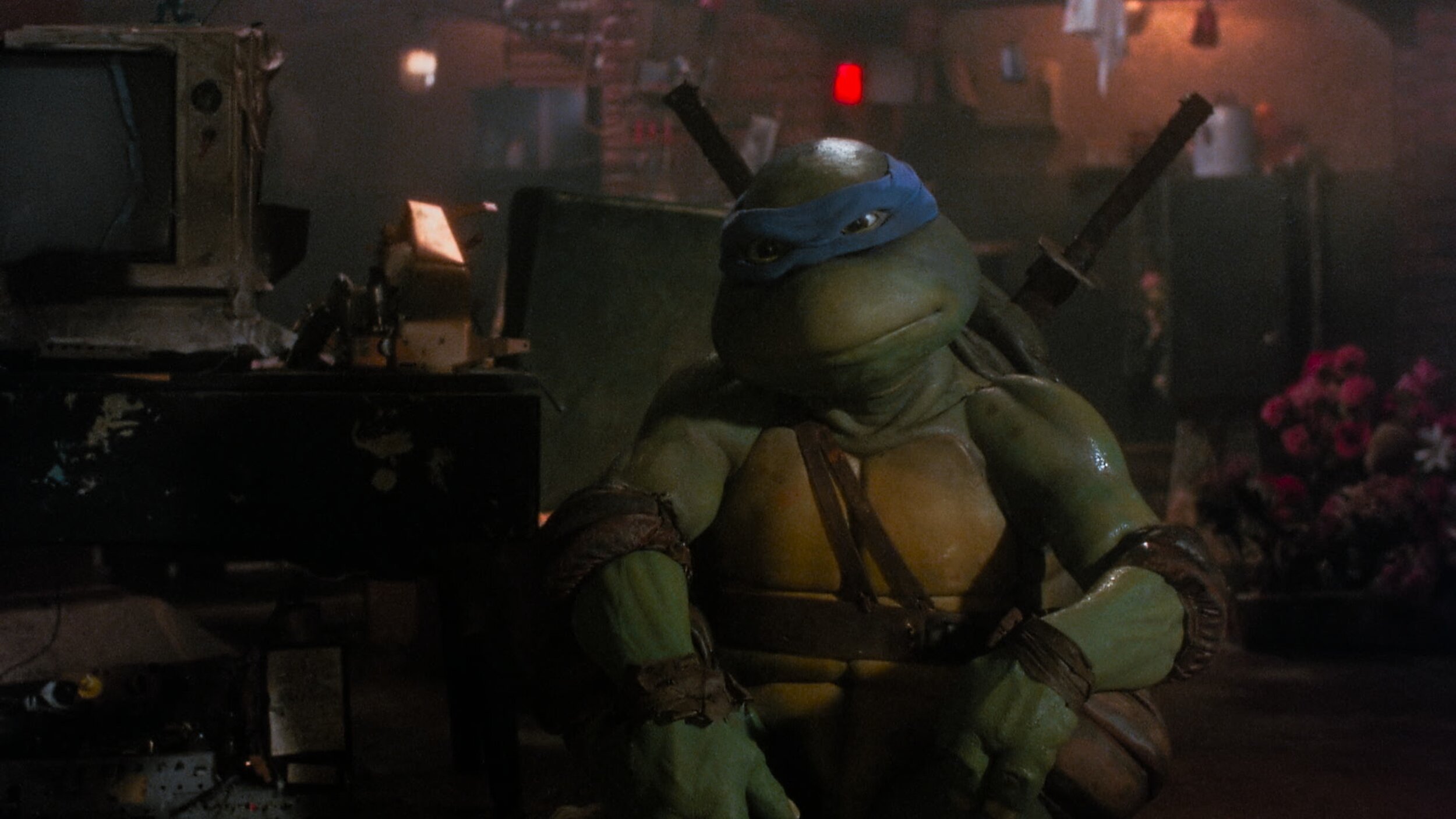
Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles
For those of you that don’t know the Ninja Turtles are near and dear to me. Not only was I a child of the 80s, but my Father was in charge of the postproduction on the original cartoons. He also wrote and directed many of them. When this came up for a remaster, I jumped at the chance to get back to my roots.
This film only required an SDR remaster. The output delivery was to be P3 D65 2.6 gamma. I set up the job using Baselight’s color management and worked in T-Log E_Gamut. The DRS was performed by Prasad with additional work by yours truly BECAUSE IT HAD TO BE PERFECT!
There were two main color hurdles to jump through. First, some scenes were very dark. I used Baseligt’s boost shadow tool to “dig” out detail from the toe of the curve. This was very successful in many of the night scenes that the film takes place in.
Another trick I used was on the Turtle’s skin. You may or may not know, but all the turtles have different skin colors. Also, most folks think they are green, when in fact there is very little green in their skin. They are more of an olive. To make sure the ratio of green to yellow was correct I converted to LAB and graded their skin in that color space. Once happy, I converted it back to T-Log E-Gamut. LAB is a very useful space for affecting yellow tones. In this space, I was able to tweak their skin and nothing else. Sort of like a key and a hue shift all in one.
The SDR ended up looking so good that the HDR was finished too. The HDR was quick and painless because of Baselight’s built-in color management. Most of the heavy lifting was already done and only a few tweaks needed.
Space Jam
Space Jam was a formative film from my youth. Not only did I have Jordan’s at the time, but I was also becoming a fledgling animation nerd (thanks Dad) when this film was released.
I set up the project for ACES color management with a Kodak LMT that I had used for other films previously. This reigned in the extreme edge of gamut colors utilized in the animation.
The biggest challenge on this project was cleaning up some of the inherent artifacts from 1990’s film recording technology. Cinesite performed all of the original composites, but at the time they were limited to 1k film recording. To mitigate that in a 4k world, I used Baselight’s texture equalizer and convolutional sharpen to give a bit of snap back to the filmed out sections.
Vishal Chathle supervised the restoration for the studio. Vishal and I boosted the looney tunes to have more color and take advantage of the wider gamut. The standard film shots, of which there were few, were pretty straightforward. Corrected mostly with Baselight’s Basegrade. Basegrade is a fantastic tool where the corrections are performed in linear gamma. This yields a consistent result no matter what your working space is.
Joe Pytka came in to approve the grade. This was very cool for me since not only did I grow up watching this film of his, but also all those iconic Superbowl commercials from the 90’s that he did. A true master of camera. He approved the grade but wished there was something more we could do with the main title. The main title sequence was built using many video effects. To recreate it would have cost a fortune. We had the original film out of it, but it looked pretty low res. What I did to remedy this was to run it through an AI up-rezer that I coded a while ago for large format shows.
The results were astounding. The titles regained some of their crisp edges that I can only presume were lost from the multiple generations of opticals that the sequence went through. The AI was also able to fix the aliasing inherent in the low res original. In the end, I was very proud of the result.
The last step was grain management. This show needed special attention because the grain from the Jordan plate was often different from the grain embedded in the animation plate that he was comped into. In order to make it consistent. I ran two de-grain passes on the scan. The first took care of the general grain from the original neg. The second pass was tuned to clean up Jordan’s grain that had the extra layer of optical grain over the top. It was a complicated noise pattern to take care of. Next, I took the two de-grained plates, roto’ed out Jordan, and re-comp-ed him over the cleaned-up plate. This gave consistency to the comps that were not there in the original.
Another area where we helped the comps were in animation error fixing. Some shots had layers that would disappear for a couple of frames, or because it was hand-drawn, a highlight that would disappear and then reappear. I used Baselight’s built-in paint tool to repair the original animation. One great feature of the paint tool is its ability to paint on two’s. An old animation trick is to only animate at 12fps if there isn’t a lot of motion. Then you shoot each frame twice. This halves the number of frames that need to be drawn. When I was fixing animation issues I would make a paint stroke on the frame and Baselight would automatically hold it for the next one. This cut down my work by half just like the original animators!
I was honored to help restore this piece of animation history. A big thanks to Michael Borquez and Chris Gillaspie for the flawless scanning and deep investigation of the best elements to use. Also a tip of the cap to Vishal Chathle for all the hard work and lending me his eagle eye!
Final Thoughts
Restoration Colorist should be a credit on its own. It’s unfortunate that this work rarely gets recognized and even less frequently gets credit. It is hard enough to deliver a director’s artistic vision from scratch. It’s arguably even harder to stay true to it 30 years later. Thanks for reading and check out these projects on HBO Max soon!
Recommendations for Home Color System
I have recently had a lot of inquiries about setting up a home color system. Even with the vaccines rolling out, I think coloring at home will stick around. There is no substitute for a full DI bay with best-in-class equipment, but this is some of the gear that I use when at home.
Color Correction Panels
These will vary based on the software used but here are the ones that I think give you the most bang for your buck when using Baselight, Resolve and others.
Filmlight Slate
Now I love my BlackBoard 2, but if desk real estate is at a premium the Slate is the next best thing. The great thing about this panel is it can double as a remote option for daylight when on set. The downside is this panel only works with Filmlight software.
Blackmagic Micro
I find that I use the mouse a lot more when working in Resolve. For that reason, I like the Micro panel more than the Mini. The Micro gives you just the basics, but the additional features the Mini has do not justify the premium paid. I think you are better off getting a Stream Deck and mapping the missing buttons to that. Controlling curves in Resolve is still best done with the mouse in my opinion. Just like the Filmlight offering, these panels only work with Resolve.
Tangent Elements
If you are like me then you probably use multiple software packages to complete your work. One great aspect of the Tangent Panels is that they work with many different types of software. An honorable mention goes out to the Ripple, especially if you are looking for a small footprint at an entry-level price.
Tangent Ripple Panel. Works with Mistika, Resolve, Flame, Lustre, Premiere, Scratch, Red Cine, Nucoda, Quantel
Monitoring
Get a Sony X300 if you can find one and afford it. That said not everyone has 30k to invest in their home setup. The LG CX has one of the best price-to-performance ratios out there. You won’t be hitting 1000nits but the color can be calibrated to be extremely close to the x300. Thanks to Dado for making this video that has all manufacture codes to unlock this display’s true potential and a walkthrough on Calman calibration.
I’m also excited to test the new displays from LG display. The next-gen LG panels found in the Sony A90j and LG G1 can achieve over 1000 nits. I’m expecting the same colorimetry performance with increased brightness. I will let you know what my real-world measurements are once I get my hands on these.
I don’t do affiliate links and am not paid by any of the manufacturers listed here. I just wanted to let everyone know what I’m using these days in the home office. Let me know what you all are using and if you have any hacks that you find helpful. Thanks for reading!
Baselight Tips and Tricks
Hey everybody! Here is a video that Filmlight just released on their website. It’s a great series and I’m happy to have contributed my little bit. Let me know what you think.
VHS Shader
A show that I’m currently working on was asking about a VHS look. It made me think of a sequence I did a while ago for Keanu shot by Jas Shelton. In This sequence, we needed to add Keegan-Michael Key to the Faith music video by George Michael.
Often, as colorists, we are looking to make the image look the best it can. This was a fun sequence because stepping on an image to fit a creative mood or period is sometimes harder then making it shinny and beautiful. When done correctly (I’m looking at you Tim and Eric Awesome Show Great Job) it can be a very effective tool for storytelling.
We uprezed the Digibeta of the music video. I then used a custom shader to add the VHS distress to the Arri Alexa footage of Key. I mixed the shader in using opacity until it felt like it was a good match. Jas and I wanted to go farther, but we got some push back from the suits. I think in the end the sequence came out great and is one of my favorite parts of the film… and the gangster kitty of course! Please find the shader used below if you would like to play.
alllll awwwww Keanu!
How To - AAF and EDL Export
AAF and EDL Exporting for Colorists
Here is a quick howto on exporting AAFs and EDLs from an Avid bin. Disclaimer - This is for colorists, not editors!
Exporting an AAF:
First, open your project. Be sure to set the frame rate correctly if you are starting a new project or importing a bin from another.
Next, open the bin that contains the sequence you want to export an AAF from.
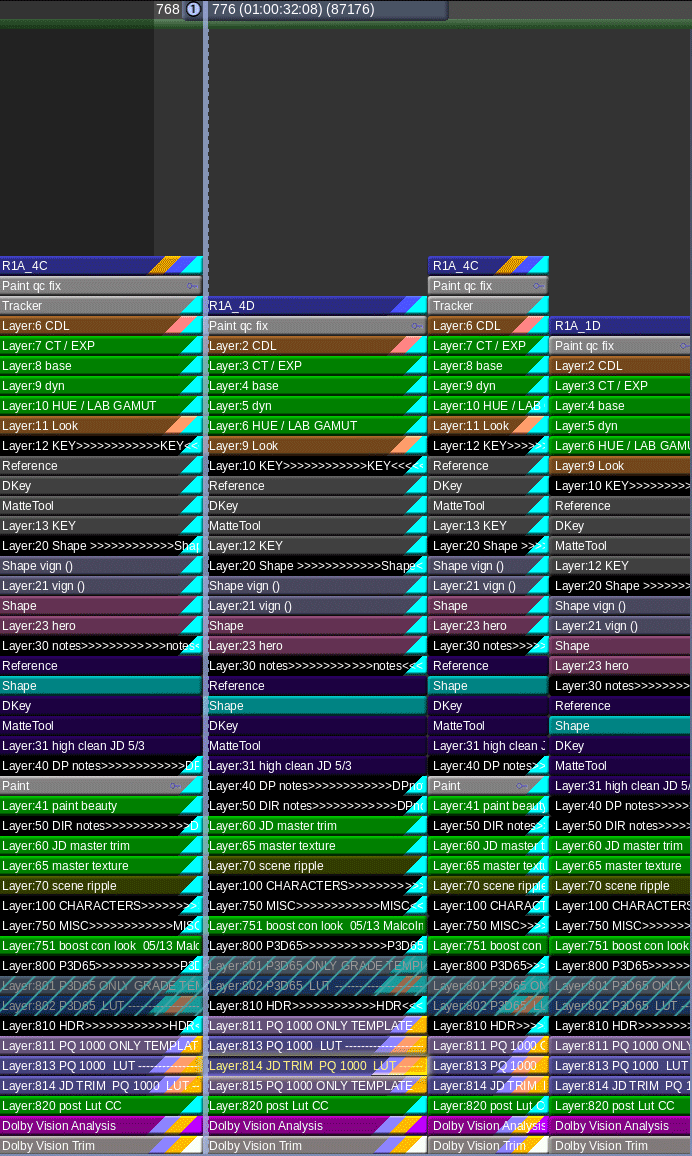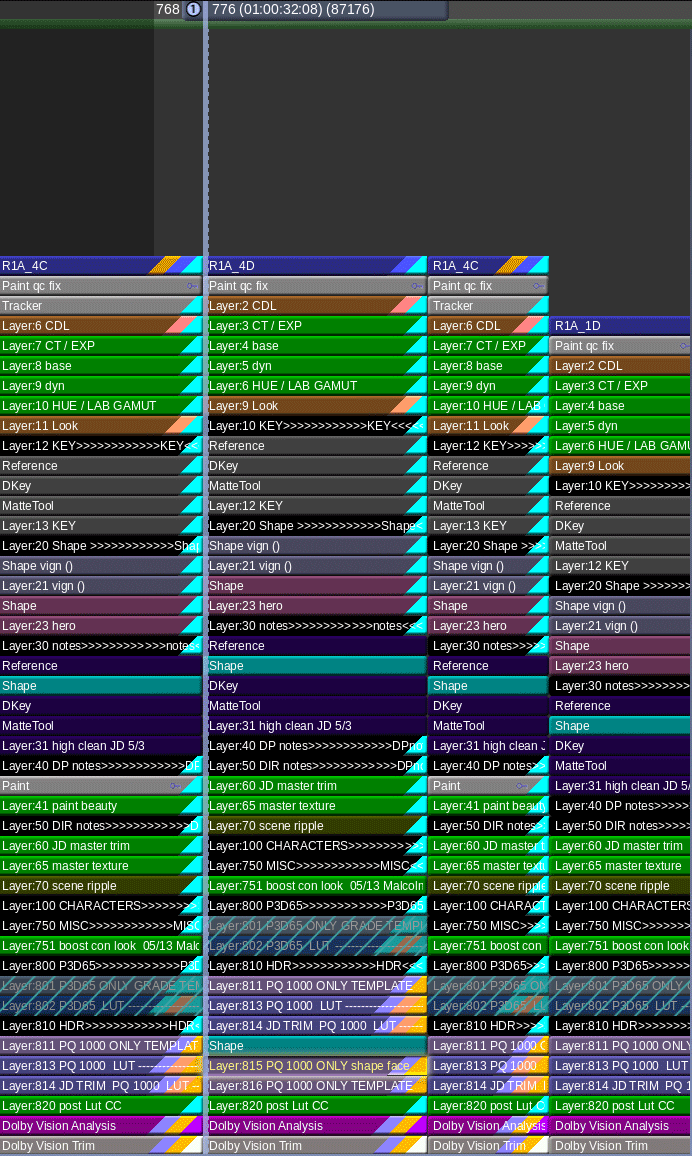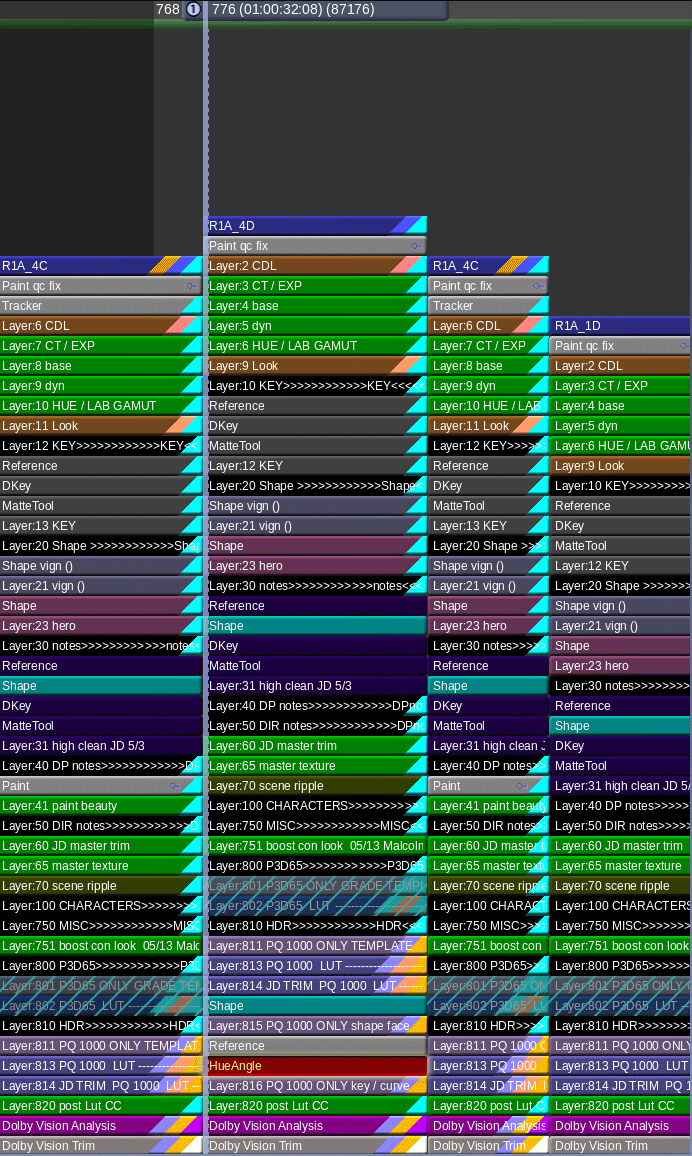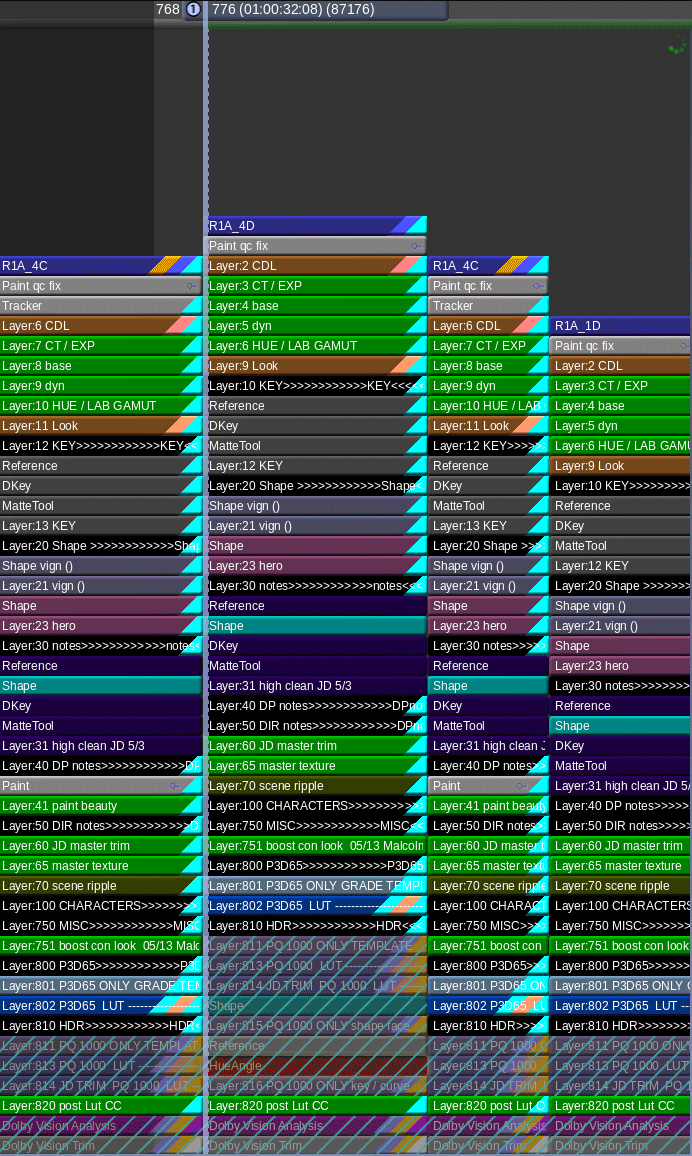
Select the timeline and right click it. This sequence should already be cleaned for color. Meaning, camera source on v1, opticals on v2, speed fx on v3, vfx on v4, titles and graphics on v5.
After you right click, go “Output” -> “Export to File”
Navigate to the path that you want to export to.. Then, click “Options”
In the “Export As” pulldown select “AAF.” Next, un-check “Include Audio Tracks in Sequence” and make sure “Export Method:” is set to “Link to(Don’t Export) Media.” Then click “Save” to save the settings and return to the file browser.
Give the AAF a name and hit “Save.” That’s it! Your AAF is sitting on the disk now.
Exporting an EDL:
We should all be using AAFs to make our conform lives easier, but if you need an EDL for a particular piece of software or just want something that is easily read by a human, here you go.
Setup the project and import your bin the same as an AAF. Instead of right-clicking on the sequence, go -> “Tools” -> “List Tool” and it will open a new window. I’m probably dating my self, but back in my day, this was called “EDL Manager.” List Tool is a huge improvement since it lets you export multi-track EDLs quickly.
Select “File_129” from the “Output Format:” pull-down. This sets the tape name to 129 characters (128+0 =129) which is the limit for a filename in most operating systems. Next, click the tracks you want to export.
Double-click your sequence in the bin to load your timeline into the record monitor. Then click “Load” in the “List Tool” window. At this point, you can click “Preview” to see your EDL in the “Master EDL” tab. To save, click the “Save List” pull-down and choose “To several files.” This option will make one EDL per video track. Choose your file location in the browser and hit save. That’s it. Your EDLs are ready for conforming or notching.
Alternate Software EDL Export
That’s great John, but what if I’m using something else other than Avid?
Here are the methods for EDL exports in Filmlight’s Baselight, BMD DaVinci Resolve, Adobe Premiere Pro, and SGO Mistika in rapid-fire. If you are using anything else… please stop.
Baselight
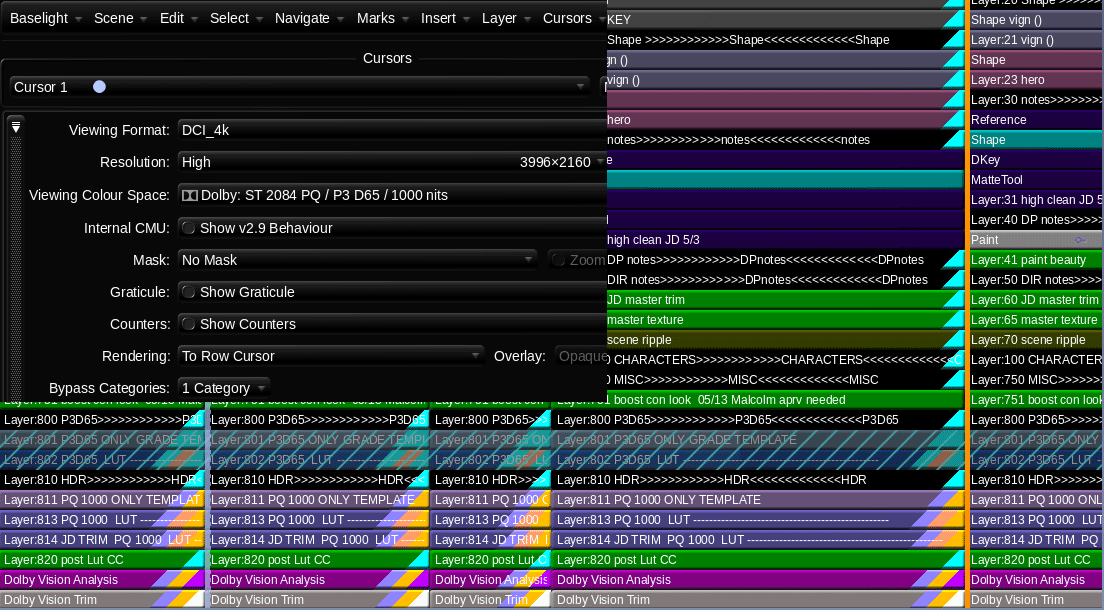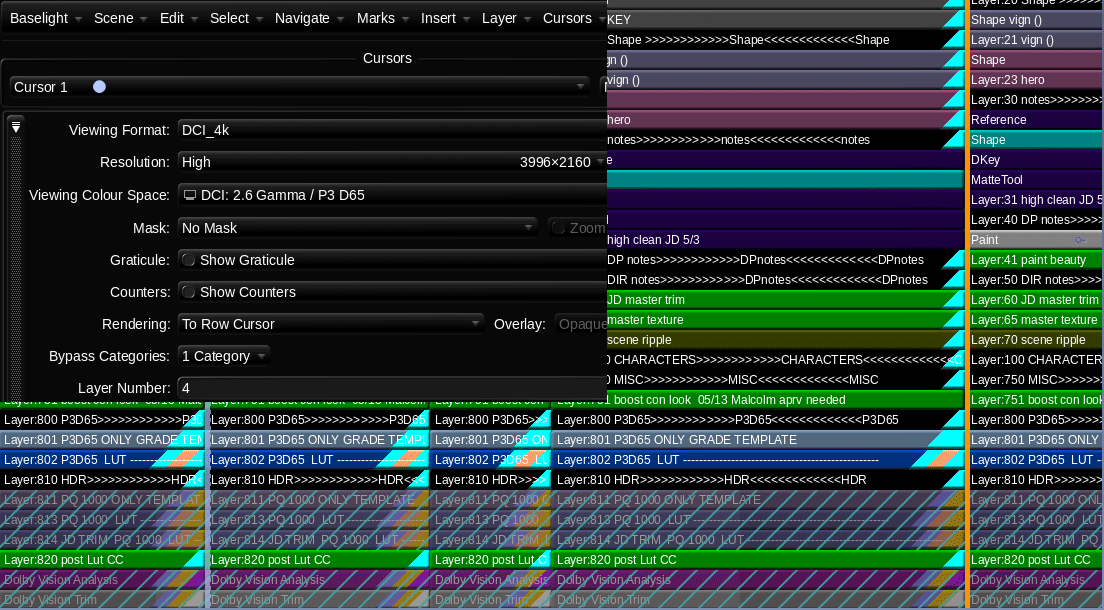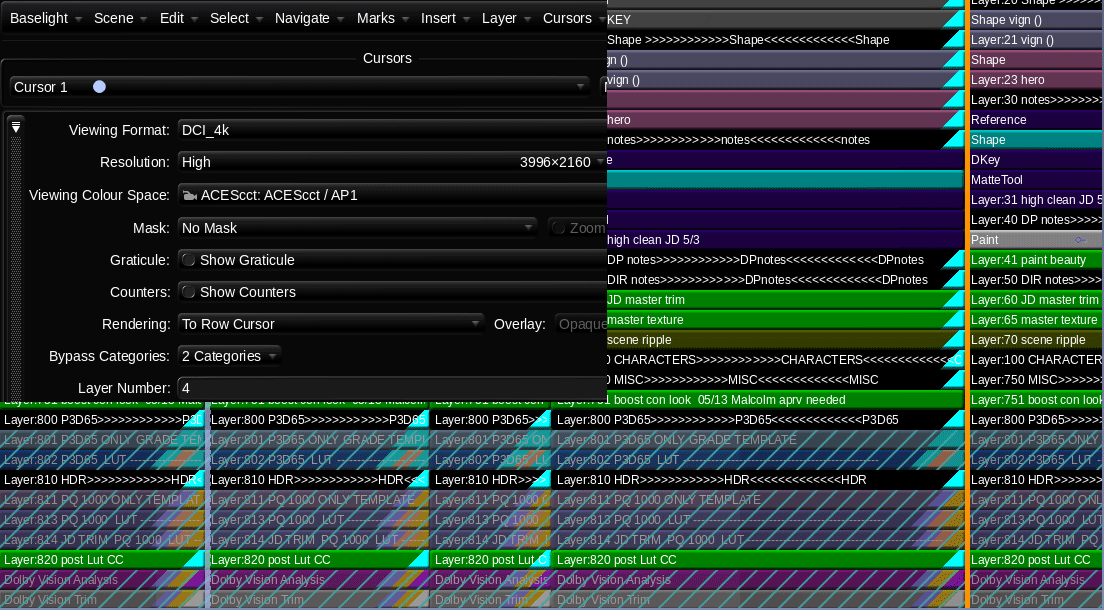
Open “Shots” view(Win + H) and click the gear pull-down. Next click “Export EDL.” The exported EDL will respect any filters you may have in “Shots” view, which makes it a very powerful tool, but also something to keep an eye on.
Resolve
In the media manager, right-click your timeline and select “Timelines“ -> “Export“ -> “AAF/XML/EDL“
Premiere Pro
Make sure your “Tape Name” column is populated.
Make sure to have your Timeline selected. Then go, “File“ -> “Export“ -> “EDL“
The most important setting here is “32 character names.” Sometimes this is called “File32” in other software. Checking this insures the file name in it’s entirety(as long as it’s not longer then 32 characters) will be placed into the tape id location of the EDL
Mistika
Set your marks in the Timespace where you want the EDL to begin and end. Then select “Media“ -> “Output“ -> “Export EDL2” -> “Export EDL.“ Once pressed you will see a preview of the EDL on the right.
No matter what the software is, the same rules apply for exporting.
Clean your timeline of unused tracks and clips.
Ensure that your program has leader and starts at an hour or ##:59:52:00
Camera source on v1, Opticals on v2, Speed FX on v3, VFX on v4, Titles and Graphics on v5
Many of us are running lean right now. I hope this helps the folks out there who are working remotely without support and the colorists who don’t fancy editorial or perhaps haven’t touched those tools in a while.
Happy Grading!
JD